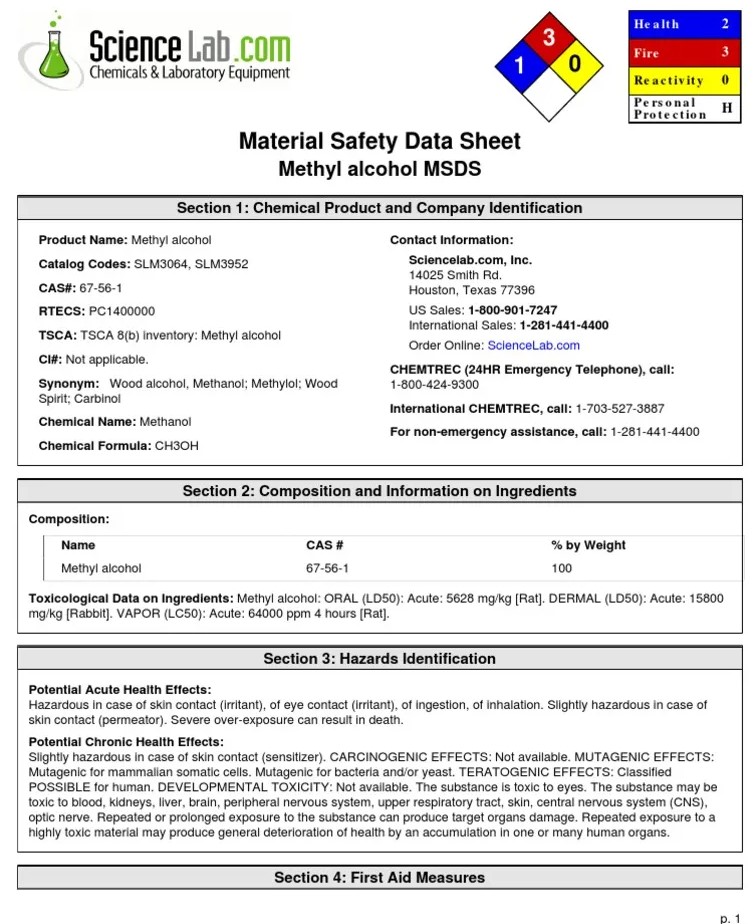
Methanol Safety Data Sheet
What is Methanol?
Methanol is known as the most basic and pure type of alcohol by its chemical formula (CH₃OH). It is a colorless and volatile chemical compound with flammable properties. It is often used for various purposes in chemistry, industry and many other sectors. However, due to its high toxicity, it is necessary to take the necessary precautions and be very careful when using it.

Properties of Methanol
- Chemical formula: CH₃OH
- Molecular weight: 32.04g/mol
- Physical appearance: Colorless, clear liquid
- Odor: Light, alcohol-like
- Boiling point: 64.7 °C
- Flash point: 11°C (high flammability)
- Solubility: Completely soluble in water, ethanol and ether
Where Is Methanol Used?
The places where methanol is used, which is used in many different fields, are as follows;
1. As A Fuel
Methanol is used as a fuel additive in the aerospace industry and even in some racing vehicles. In biodiesel production, it can be used as a solvent.
2. Industrial Solvent
Another one of the areas where methanol usage is high is industrial solvent production. It is used in the production of paints, plastics, and resins and in printing applications. In laboratories, it can also be used as a solvent.
3. Antifreeze and Window Cleaner
The use of methanol as an alternative to ethylene glycol in anti-freezing liquids is also common. Automotive window cleaner production is also among the areas of methanol use. Decontamination.
4. Chemical Synthesis / Laboratory
Methanol is also preferred as a raw material. It is used as a raw material in the production of formaldehyde, acetic acid and other chemicals.
5. Pharmaceutical and Pharmaceutical Industry
It is used as a solvent and reagent in the production of antibiotics, vaccines and vitamins, and can be used as a flammable substance in pharmaceutical tablet coating processes.
6. Energy Production
Coal can be processed in gasification plants. Its use as a hydrogen carrier in fuel cells is also under investigation.
7. Food Industry (Indirect Use)
There is also indirect use. It is used indirectly in the production of food packaging materials (PET plastics) and in the disinfection of food processing equipment.
8. Industry and electronic Industry
There is the use of methanol as a cleaning agent in the production of semiconductors and circuit boards, and in the chemical process steps in the production of LCD screens.
9. Leather and Textile
As a degreaser in leather processing processes, it acts as a catalyst in the production of synthetic fibers
What are the Methanol Storage Conditions?
- Suitable Materials: Stainless steel or polyethylene tanks.
- Storage Temperature: Between 15-30 Decc, should be protected from direct sunlight.
- Interaction with Prohibited Substances:
- It should not be kept in the same environment as oxidizers (nitric acid, hydrogen peroxide).
- Contact with aluminum and magnesium leads to corrosion.

What are the Environmental Effects of Methanol?
Methanol is a substance that can have a negative impact on human health, as well as negative consequences for environmental and waste management. For this reason, the Methanol Safety Data Sheet is very important.
Environmental Harms: It can lead to soil and water pollution, biodegradation is slow.
Waste Management: Since it is in the hazardous waste class, it must be delivered to licensed disposal companies.In Case of Spillage: It should be collected by impregnationwith sand or inert material, never mixed into the sewer.
What are the Methanol Alternatives and Their Comparison with Methanol
There are 2 substances that come to mind in the first place that can be used as an alternative to methanol use. These substances are Ethanol and Isopropyl Alcohol. Both of these substances have lower toxicity than methanol. In the same way, they are lower in flammability than methanol. Methanol is at a very high flammable level. However, in contrast to toxicity and flammability, methanol is cheaper than both ethanol and isopropyl acid when viewed as an industrial cost. For this reason, it is used industrially more often and more often than the other two substances.
| Feature | Methanol | Ethanol | Isopropyl Alcohol |
| Toxicity | High | Middle | Low |
| Flammability | Very high | High | High |
| Industrial Cost | Low | High | Middle |
Occupational Exposure Limits in the Use of Metonal:
OSHA PEL (Permissible Exposure Limit): 200 ppm (8-hour average)
ACGIH TLV: 200 ppm (Risk of skin absorption!)
Respiratory Protection: Mask with organic vapor filter (NIOSH approved) is mandatory.
Workplace Controls: Ventilation systems and LEL (Lower Explosive Limit) detectors should be used.

How Is Methanol Used?
Although the use of methanol varies according to the sector, production, manufacturing, construction, etc. it is used for many purposes. On the other hand, it is for the intended use that determines the way methanol is used. Methanol can be used in pure form or by combining it with different substances.
However, there is a point that should be paid attention to at this point as well. Since the toxic and hazard ratio will increase even more in the case of using methanol with different substances, people who are experts in their field should do this job.
What is Methanol Poisoning?
As with almost all chemical substances, there are some issues that we should pay attention to when using methanol. Methanol can cause serious poisoning when ingested, full or in direct or indirect contact with the skin. However, when used in various compounds, it can cause different damages to the body and irritate the skin.
What are the Symptoms of Methanol Poisoning?
There are some symptoms that we can take into account when we suspect methanol poisoning. At the beginning of these, headache and dizziness come, the first effect with its pungent smell and content may be in the form of rotation at first.
Other symptoms of methanol poisoning are;
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Visual disturbances (Blurred vision, temporary/permanent blindness)
- Loss of consciousness
- Respiratory problems, respiratory arrest
Symptoms may be observed in the form. Although it varies from person to person, there may also be different symptoms of poisoning. For this reason, you should definitely use the necessary equipment and take the necessary precautions before using methanol. Methanol Safety Data Sheet should definitely include the equipment you need touse and the first aid you need to apply.
Dangerous Reactions that Methanol Can Cause
In addition to methanol poisoning, it can exhibit an explosive reaction when it reacts with combustion and acids due to its flammability. These reactions can sometimes be controlled, and sometimes they can have consequences that are very difficult to control. The easiest way to prevent these reactions is, of course, Methanol Safety Data Sheet.
- Combustion Reaction:
2CH₃OH + 3O₂ → 2CO₂ + 4H₂O
dicate: If it does not burn completely, deadly by-products such as formaldehyde and carbon monoxide are formed. - Reaction with Acids: Forms dimethyl ether withsulfuric acid (explosive risk).
How is Emergency Intervention Performed in Methanol Poisoning?
In case of metabolic poisoning, you should definitely call the emergency help line to explain the situation and request an ambulance. Until the ambulance arrives, you should first calm down and take environmental safety when performing the first and emergency intervention.
Ingestion of methanol is one of the most common and dangerous situations in methanol poisoning. In this case, you should seek medical help immediately, and you should not make the person who swallowed vomit until medical help arrives.
Inhalation of methanol, inhalation of methanol due to the fact that methanol is a volatile chemical component is also another common way of poisoning. Jul Jul In cases of poisoning caused by inhalation of methanol, it is necessary to get out into the fresh air and get fresh air without wasting time. On the other hand, it is necessary to intervene to provide oxygen support in the fastest way and minimize the damage of inhaled methanol.
In case of methanol contact with the skin, you should wash the contact area with plenty of soap and water and minimize the damage of methanol to the skin.
If it is not used correctly and the necessary safety measures are not taken, methanol poisoning can lead to life-threatening hazards.

Methanol Safety Data Sheet
| Episode | SUBHEADING | DESCRIPTION / VALUES | SECURITY MEASURES |
| 1. describing | Chemical Name | Methanol (Methyl Alcohol) | — |
| CAS No | 67-56-1 | — | |
| EC No | 200-659-6 | — | |
| 2. DANGERS | GHS Pictograms | Flame, Toxic, Skin Irritation | No contact with the flame is allowed! |
| H-Phrases (Risks) | H225: Flammable liquid H3 01: Ingestion Lethal H3 11: Skin contact toxic | Work in a ventilated area. | |
| 3. composition | The Ratio of Pure Methanol | ≥ %99.5 | — |
| 4. first aid | Ingestion | Seek medical attention immediately. Don’t Make me vomit. | If there is a smell of alcohol in the mouth, contact the emergency department. |
| Skin Contact | Wash with plenty of soap and water for 15 minutes. | Remove contaminated clothing. | |
| Eye Contact | Rinse with water for 15 minutes, keeping the eyelid open. | If he is wearing a lens, remove it. | |
| 5. fire | Extinguishing Agents | Dry chemical powder, CO₂, foam | Do not use water! (It can spread) |
| Explosion Risk | Flash point: 11°C | Protect from static electricity. | |
| 6. ACCIDENT STATUS | Spill Measures | Collect with absorbent material (sand, clay). | Use gloves and glasses. |
| 7. storage | Favorable Conditions | Cool, dark, ventilated area. | Keep away from oxidizers. |
| 8. PPE | Mandatory Equipment | Nitrile gloves, chemical glasses, FFP3 mask | Avoid skin contact. |